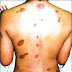
Acne is a skin condition that occurs due to the overproduction of oil by the oil glands of the skin. The oil that normally lubricates the skin gets trapped in blocked oil ducts and results in what we know as pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads on the surface of skin. Sometimes it also includes deeper skin lesions that are called cysts.
Pimples are small skin swellings that sometimes contain pus.
Blackheads are dark formations on the skin due to an accumulated mixture of oil and cells in a blocked skin pore.
Whiteheads are small flesh-or white-colored bumps due to skin pore blockage.
Cysts are closed sacs beneath the skin or deeper that contain fluid or semisolid substances.
The areas of the skin that are most susceptible to acne are those areas that contain the largest number of oil glands. For example, it is estimated that there are 2,000 oil glands per square inch on the forehead alone. The face, chest, shoulders, and back are the areas with the highest population of oil glands.
Acne commonly occurs in people between their teenage years and their 20s. However, it is not restricted to this age. Older adults and children can also have acne.
What Causes Acne?
There are four major factors responsible for causing acne. They act together to cause the characteristic pimples, whiteheads and blackheads associated with acne. They are:
Overactive Oil Glands
Oil glands are located deep in the skin. They are also known as sebaceous glands.
Each oil gland is connected to a tiny canal that contains a hair. The canal with its contained hair is called a follicle.
The glands produce oil (also known as sebum) that flows to the surface of the skin through these canals to lubricate the hair follicles and the surrounding skin.
The opening of the canal with the attached hair (follicle) onto the skin is the skin pore.
The oil glands vary in size, and the larger ones are associated with visible skin pores.
The oil glands are stimulated to produce oil by hormones, specifically the male hormones called androgens (women also have these hormones, but much less of them). These hormones are produced by the testes in men and by the ovaries in women. In both sexes, androgens are also produced by the adrenal glands.
During times of stress, the adrenal glands produce increased levels of these hormones, causing even greater enlargement of the oil glands.
During puberty, the oil glands become overactive in response to hormonal changes.
Blockage Of The Skin Pores
Oily skin occurs when an overactive oil gland enlarges and overproduces oil. Acne develops when some of the pores (through which oil normally flows from the oil gland to reach the skin surface) become blocked, resulting in trapping of oil within the skin pores.
The pores are blocked by skin cells that have been shed from the lining of the skin pore and have bunched together. The cause for this clogging is not known, but it is not due to poor hygiene. A blackhead or whitehead will develop from this skin pore blockage
Although acne is not caused by a bacterial infection, bacteria do play a role in making the situation worse. The bacterium Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), is a normal part of the skin surface. It keeps the skin from being invaded by harmful bacteria.
When oil is trapped in the hair follicles, the normal skin bacteria P. acnes will grow in the blocked pore. The bacteria produce chemicals that alter the composition of the oil, which makes it more irritating to the skin and causes inflammation.
Inflamed skin is characterized by redness, swelling, warmth and discomfort. Inflammation of the skin occurs because the body's immune system is acting to rid itself of a foreign substance. In the case of acne, this substance is either bacteria or the irritating compounds they have produced.
These four factors contribute to blocked skin pores, which bulge outward to form:
Blackheads. These form when the pores are clogged close to the surface of the skin. Because they are exposed to the skin surface, blackheads don't usually become inflamed. Blackheads are dark due to the presence of a dark pigment. This color is not the result of dirt in the pores.
Whiteheads. These develop from a blockage deeper in a pore. Lacking a drainage path, the oil accumulates in the skin, causing small flesh-colored or white-colored bumps. Unlike blackheads, whiteheads are more likely to lead to the red inflammations known as pimples or zits.
Pustules (also known as pimples or zits) occur when the walls of the blocked follicle ruptures. Oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria normally found on the skin surface get into the skin and irritate it, forming small areas of inflammation.
Cysts are larger, red, inflamed areas deep in the skin that indicate a more extensive infection.
Who Gets Acne?
Adolescents are the most commonly affected. Because of the high hormonal activity during puberty, acne affects many teenagers. Those individuals whose oil glands produce more oil tend to be affected by acne more often than those whose glands don't produce excess oil.
Heredity Can Play A Role
Statistics suggest that heredity is a strong contributing factor for acne. A family history of acne means that there probably is a genetic basis for the condition.
How Is Acne Treated?
Acne responds well to treatment, especially if treated early, at the onset of the condition.
Treatment is offered to:
Prevent possible scarring
Deal with inflamed and painful areas
Limit the formation of new blackheads and whiteheads
Lessen any stress or embarrassment associated with the acne