Fortunately, there are several strategies to help people cope with vitiligo. Also, various treatments which we will discuss a bit later than minimize, camouflage, or, in some cases, even eliminate white patches.
Talking with other people who have vitiligo may also help. The National Vitiligo Foundation can provide information about vitiligo and refer you to local chapters that have support groups of patients, families, and physicians.
Family and friends are another source of support. Some people with vitiligo have found that cosmetics that cover the white patches improve their appearance and help them feel better about themselves. You may need to experiment with several brands of concealing cosmetics before finding the product that works best.
Why the skin turns white?
The skin is made up of two main types of cells or building blocks: keratinocytes and melanocytes. The keratinocytes make up the bulk of the skin. The melanocytes are the cells that make the skin color.
In people with vitiligo disease, the immune cells (cells which fight infection) attack the melanocytes and kill them. When the melanocytes in a certain area die, the skin turns white.

No one knows exactly why the immune cells attack the melanocytes in people with vitiligo disease
The cause of vitiligo is not yet fully known but many think that it is a disease in which the body makes antibodies to its own melanocytes, and in doing so destroys them.
How are vitiligo victims affected?
This disease affects all races, men and women and all age groups. Obviously, it is more noticeable in people with dark skin.Half the people who have vitiligo disease develop it before age 20; most develop it before their 40th birthday.
Vitiligo disease attacks the soul and psyche.
"When was the last time you saw someone with vitiligo handling your food? It is the public's image that it is some leprosy-type of disease," a vitiligo victim once said.A lot of folks feel this disease has trapped them and kept them away from their life goals.
What are the symptoms of vitiligo disease?
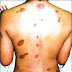
The main symptom of vitiligo disease is pigment loss that produces milky-white patches (depigmentation) on your skin. These milky-white patches usually do not itch or hurt.

Other less common signs may include:
· Premature whitening or graying of the hair on your scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows or beard
· Loss of color in the tissues that line the inside of your mouth (mucous membranes)
· Loss or change in color of the inner layer of your eye (retina)
. Although any part of your body may be affected by vitiligo, depigmentation usually first develops on sun-exposed areas of your skin, such as your hands, feet, arms, face and lips. The spots are more common over bony areas.
· Other d the mouth, eyes, nostrils, navel, genitals, and rectal areas.
Vitiligo common areas for white patches to appear are the armpits and groin, and aroun generally appears in one of three patterns:
1. Focal pattern — the depigmentation is limited to one or only a few areas
2. Segmental pattern — depigmented patches develop on only one side of the body.
3. Generalized pattern — the most common pattern. Depigmentation occurs symmetrically on both sides of the body.

In addition to white patches on the skin, people with vitiligo may have premature graying of the scalp hair, eyelashes, eyebrows, and beard. People with dark skin may notice a loss of color inside their mouths.
Although it can start at any age, vitiligo often first appears between the ages of 20 and 30.
The white patches may begin on your face above your eyes or on your neck, armpits, elbows, genitalia, hands or knees. They're often symmetrical and can spread over your entire body.
The disorder affects both sexes and all races equally.Most people with vitiligo disease are otherwise healthy and have normal skin texture and sensation. However, the condition may be more common in people with certain autoimmune diseases - diseases in which your immune system reacts against your body's own organs or tissues - such as Addison's disease, vitamin B-12 deficiency anemia (pernicious anemia), or thyroid disorders, including hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.The natural course of vitiligo disease is difficult to predict. Sometimes the patches stop forming without treatment. In other cases, pigment loss can involve most of the surface of your skin.
Is the Depigmented Patches Spread?
Focal pattern vitiligo and segmental vitiligo remain localized to one part of the body and do not spread. There is no way to predict if generalized vitiligo will spread. For some people, the depigmented patches do not spread. The disorder is usually progressive, however, and over time the white patches will spread to other areas of the body.
For some people, vitiligo disease spreads slowly, over many years. For other people, spreading occurs rapidly. Some people have reported additional depigmentation following periods of physical or emotional stress.

What are the possible causes of vitiligo disease?
The scientific and medical communities readily admit that the precise cause of vitiligo disease is complex and not fully understood.The cause of vitiligo disease is not known, but doctors and researchers have several different theories
1 . Genetic susceptibility. This is the theory that the susceptibility or predisposition to vitiligo is genetic, and that some defect in the genetic structure, makes people more susceptible to vitiligo. While we do see vitiligo in more than one family member about 20% of the time, about 80% of patients report no other family members with vitiligo. Many experts agree that not everyone who is susceptible to vitiligo will necessarily develop it. As with all genes, people may carry the defect that causes vitiligo, and even pass it on to their children, without ever developing vitiligo themselves. Thus other factors, including environmental and personality factors, may play a role in the onset (beginning) of vitiligo.
2. Autoimmune disease. The most widely accepted view is that the depigmentation occurs because vitiligo is an autoimmune disease. This does not necessarily represent a weak or deficient immune system, but one which may be malfunctioning or misdirected.The human body is made of tiny building blocks called cells. One group of cells are called immune cells. These are the cells that normally fight off infection and germs. Another type of cell is the melanocyte. These are the cells that produce pigment molecules which give the skin its color. Vitiligo occurs when the immune cells start attacking and killing the melanocytes. As the melanocytes die, the skin turns white because it no longer has melanocytes making pigment or color. No one knows why the immune cells attack and kill the melanocytes in patients with vitiligo.Another theory is that melanocytes, the cells that produces skin pigment destroy themselves.

3. Oxidative Stress. This is one theory about what may cause or contribute to the onset or exacerbation of vitiligo. Oxidative stress is an over-accumulation of hydrogen peroxide in the skin. Every person develops hydrogen peroxide in the skin, as a result of natural biological processes. An enzyme called "catalase" normally breaks down the hydrogen peroxide in the skin into water and oxygen. However, some people with vitiligo may have a problem manufacturing, using or delivering catalase to the skin.4. There are alternative theories about vitiligo that suggest diet, nutrition, and digestive disorders may play a role in the destruction of melanocytes. Some believe that internal pathogens within the digestive tract, such as yeast proliferation, might relate to vitiligo.

5. Vitiligo has been associated with certain diseases such as hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, Addison's disease, pernicious anemia, alopecia areata.
6. Exposure to certain chemicals can cause vitiligo. Some chemicals, particularly photography chemicals such as Phenols, can trigger vitiligo in those who are susceptible. Phenols can also be found in many types of hair colorings, household stains, and similar products. There are other industrial chemicals and substances which may also trigger the onset of vitiligo.

7. Finally, some people have reported that a single event such as sunburn or emotional distress triggered vitiligo; however, these events have not been scientifically proven as causes of vitiligo.
It should be noted that none of these theories has been proved to be a definite cause of vitiligo. However, many doctors and researchers believe that a genetic predisposition or susceptibility to vitiligo exists in most people who develop vitiligo.

How is vitiligo disease diagnosed?
The diagnosis of vitiligo disease based on a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A doctor will likely suspect vitiligo if you report (or the physical examination reveals) white patches of skin on the body—particularly on sun-exposed areas, including the hands, feet, arms, face, and lips.
If vitiligo is suspected, the doctor will ask about your medical history. Important factors in the diagnosis include a family history of vitiligo; a rash, sunburn, or other skin trauma at the site of vitiligo 2 to 3 months before depigmentation started; stress or physical illness; and premature (before age 35) graying of the hair.
In addition, the doctor will ask whether you or anyone in your family has had any autoimmune diseases, and whether you are very sensitive to the sun.To help confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may take a small sample (biopsy) of the affected skin to examine under a microscope. In vitiligo, the skin sample will usually show a complete absence of pigment-producing melanocytes.
On the other hand, the presence of inflamed cells in the sample may suggest that another condition is responsible for the loss of pigmentation. Because vitiligo disease may be associated with pernicious anemia (a condition in which an insufficient amount of vitamin B12 is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract) or hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid gland), the doctor may also take a blood sample to check the blood-cell count and thyroid function.
For some patients, the doctor may recommend an eye examination to check for uveitis (inflammation of part of the eye), which sometimes occurs with vitiligo. A blood test to look for the presence of antinuclear antibodies (a type of autoantibody) may also be done. This test helps determine if the patient has another autoimmune disease.

Nice to Know:
It's important to note that not all white skin patches are vitiligo. There are other conditions and diseases which are associated with white skin, such as leprosy once called vitiligo. Albinism, Leucism, Melanism, Tinea Versicolor and Pityriasis alba are among other conditions and diseases which are associated with white skin that must be ruled out.
Clearly it seems mandatory to make the correct diagnosis. A definitive diagnosis can be carried out by using Untraviolet Wood’s Light. Vitiligo shows a very characteristic fluorescence under this condition which is absent in other skin diseases
In fair-skinned patients, Wood’s light examination in a darkened room detects vitiliginous patches; depigmented skin reflects the light, and pigmented skin absorbs it.Biopsy will show normal skin except for the absence of melanocytes.

Albinism
What are your vitiligo disease treatment options?
Obviously, the objective of treating vitiligo disease is to restore the function of the skin in order to improve the patient's appearance. Therapy for vitiligo disease takes a long time--it usually must be continued consistently for 6 to 18 months, in order to see results.
The choice of therapy depends on the number of white patches and how widespread they are and on the patient's preference for treatment. Each patient responds differently to therapy, and a particular treatment may not work for everyone.
Medical Therapies
Topical Steroid TherapySteroids may be helpful in repigmenting the skin (returning the color to white patches), particularly if started early in the disease. Corticosteroids are a group of drugs similar to the hormones produced by the adrenal glands (such as cortisone). Doctors often prescribe a mild topical corticosteroid cream for children under 10 years old and a stronger one for adults.

Patients must apply the cream to the white patches on their skin for at least 3 months before seeing any results. It is the simplest and safest treatment but not as effective as psoralen photochemotherapy (see below). The doctor will closely monitor the patient for side effects such as skin shrinkage and skin striae (streaks or lines on the skin).
Psoralen Photochemotherapy. Psoralen photochemotherapy (psoralen plus ultraviolet A therapy, or PUVA) is probably the most beneficial treatment for vitiligo available. The goal of PUVA therapy is to repigment the white patches. However, it is time-consuming and care must be taken to avoid side effects, which can sometimes be severe.Psoralens are drugs that contain chemicals that react with ultraviolet light to cause darkening of the skin. The treatment involves taking psoralen by mouth (orally) or applying it to the skin (topically).
This is followed by carefully timed exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA) light from a special lamp or to sunlight. Patients usually receive treatments in their doctors' offices so they can be carefully watched for any side effects.Patients must minimize exposure to sunlight at other times, thereafter.

UVA light activates
Topical Psoralen Photochemotherapy. Topical psoralen photochemotherapy often is used for people with a small number of depigmented patches (affecting less than 20 percent of the body).
It is also used for children 2 years old and older who have localized patches of vitiligo.
Treatments are done in a doctor's office under artificial UVA light once or twice a week. The doctor or nurse applies a thin coat of psoralen to the patient's depigmented patches about 30 minutes before UVA light exposure. The patient is then exposed to an amount of UVA light that turns the affected area pink. The doctor usually increases the dose of UVA light slowly over many weeks.

Absorbs the UV light
Eventually, the pink areas fade and a more normal skin color appears. After each treatment, the patient washes his or her skin with soap and water and applies a sunscreen before leaving the doctor's office.
There are two major potential side effects of topical PUVA therapy:
(1) severe sunburn and blistering and(2) too much repigmentation or darkening of the treated patches or the normal skin surrounding the vitiligo (hyperpigmentation).Patients can minimize their chances of sunburn if they avoid exposure to direct sunlight after each treatment. Hyperpigmentation is usually a temporary problem and eventually disappears when treatment is stopped.Oral Psoralen Photochemotherapy
Oral PUVA therapy is used for people with more extensive vitiligo (affecting greater than 20 percent of the body) or for people who do not respond to topical PUVA therapy.
Oral psoralen is not recommended for children under 10 years of age because of an increased risk of damage to the eyes, such as cataracts. For oral PUVA therapy, the patient takes a prescribed dose of psoralen by mouth about 2 hours before exposure to artificial UVA light or sunlight. The doctor adjusts the dose of light until the skin areas being treated become pink. Treatments are usually given two or three times a week, but never 2 days in a row.

Psoralea fruit
For patients who cannot go to a PUVA facility, the doctor may prescribe psoralen to be used with natural sunlight exposure. The doctor will give the patient careful instructions on carrying out treatment at home and monitor the patient during scheduled checkups.
Known side effects of oral psoralen include sunburn, nausea and vomiting, itching, abnormal hair growth, and hyperpigmentation. To avoid sunburn and reduce the risk of skin cancer, patients undergoing oral PUVA therapy should apply sunscreen and avoid direct sunlight for 24 to 48 hours after each treatment. Patients should also wear protective UVA sunglasses for 18 to 24 hours after each treatment to avoid eye damage, particularly cataracts.
Depigmentation. Depigmentation involves fading the rest of the skin on the body to match the already white areas. For people who have vitiligo on more than 50 percent of their bodies, depigmentation may be the best treatment option.Patients apply the drug monobenzylether of hydroquinone (monobenzone or Benoquin) twice a day to pigmented areas until they match the already depigmented areas.
Patients must avoid direct skin-to-skin contact with other people for at least 2 hours after applying the drug.
The major side effect of depigmentation therapy is inflammation (redness and swelling) of the skin. Patients may experience itching, dry skin, or abnormal darkening of the membrane that covers the white of the eye. Depigmentation is permanent and cannot be reversed. In addition, a person who undergoes depigmentation will always be abnormally sensitive to sunlight.

Surgical Therapies.
All surgical therapies must be viewed as experimental because their effectiveness and side effects remain to be fully defined.
Autologous Skin Grafts. In an autologous (use of a person's own tissues) skin graft, the doctor removes skin from one area of a patient's body and attaches it to another area. This type of skin grafting is sometimes used for patients with small patches of vitiligo.
doctor removes sections of the normal, pigmented skin (donor sites) and places them on the depigmented areas (recipient sites). There are several possible complications of autologous skin grafting. Infections may occur at the donor or recipient sites. The recipient and donor sites may develop scarring, a cobblestone appearance, or a spotty pigmentation, or may fail to repigment at all.Treatment with grafting takes time and is costly, and most people find it neither acceptable nor affordable.

Skin Grafts Using Blisters. In this procedure, the doctor creates blisters on the patient's pigmented skin by using heat, suction, or freezing cold. The tops of the blisters are then cut out and transplanted to a depigmented skin area.
The risks of blister grafting include the development of a cobblestone appearance, scarring, and lack of repigmentation. However, there is less risk of scarring with this procedure than with other types of grafting.
Micropigmentation (Tattooing). Tattooing implants pigment into the skin with a special surgical instrument. This procedure works best for the lip area, particularly in people with dark skin; however, it is difficult for the doctor to match perfectly the color of the skin of the surrounding area. Tattooing tends to fade over time. In addition, tattooing of the lips may lead to episodes of blister outbreaks caused by the herpes simplex virus.
Autologous Melanocyte Transplants. In this procedure, the doctor takes a sample of the patient's normal pigmented skin and places it in a laboratory dish containing a special cell culture solution to grow melanocytes. When the melanocytes in the culture solution have multiplied, the doctor transplants them to the patient's depigmented skin patches.This procedure is currently experimental and is impractical for the routine care of people with vitiligo.

Additional Therapies
People who have vitiligo disease, particularly those with fair skin, should use a sunscreen that provides protection from both the UVA and UVB forms of ultraviolet light.
Sunscreen helps protect the skin from sunburn and long-term damage. Sunscreen also minimizes tanning, which makes the contrast between normal and depigmented skin less noticeable.
Cosmetics. Some patients with vitiligo disease cover depigmented patches with stains, makeup, or self-tanning lotions.
These cosmetic products can be particularly effective for people whose vitiligo is limited to exposed areas of the body. Dermablend, Lydia O'Leary, Clinique, Fashion Flair, Vitadye, and Chromelin offer makeup or dyes that patients may find helpful for covering up depigmented patches.

Counseling and Support Groups. Many people with vitiligo disease find it helpful to get counseling from a mental health professional. People often find they can talk to their counselor about issues that are difficult to discuss with anyone else. A mental health counselor can also offer patients support and help in coping with vitiligo. In addition, it may be helpful to attend a vitiligo support group
Vitiligo – the road of healing. Our line of Medication, with our products
Vitiligo is a skin pigment disorder that affects around one percent (40 – 50 million) of the world’s population. In Vitiligo, the cells (melanocytes) within the skin that control the production of the pigment melanin are destroyed resulting in white patches of skin. Patches also appear on the tissues that line the inside of the mouth, nose and private areas, as well as the retina of the eye. White hairs also develop in these affected areas.

melanocyte
this rare skin disorder is an inherited trait, but some who suffer from the disease have reported singular events such as severe sunburn or an extremely stressful event as the root cause.
People with vitiligo often have problems with their thyroid gland; many people with vitiligo have problems with their liver.
Genuine vitiligo usually appears at the age range of 19-40 years old.
Cleansing of the body with a special attention to the liver and bowels often helps to get rid of vitiligo.
How to cleanse your body
1 – Castor oil drink internally as a stimulant laxative to relieve constipation, to cleanse the intestines for a medical procedure and detoxify stagnant food residual in gastrointestinal tract

Use half glass ( cup) of castor oil (120 ml) and add another 120 ml fresh orange juice, mix will and drink first thing in the morning. Continue using plan soup all that day and let the oil do the job, to cleanse all your GIT fully, it takes all the day and frequent visiting to washroom.
2 – Senna leaf acts as a laxative and is primarily used for constipation, preoperative cleansing and weight loss. Senna can also be used as an anti-inflammatory, for cellular regeneration.
Use 1 tea spoon of the herb, add one cup of boiling water. Leave for 10 minutes drink once daily in nighttime before you sleep.
How to improve your thyroid & liver function:
1 - Kelp powder, is an amazing supplement. It is one of the planet's richest sources of nutrients and is extremely popular especially in countries such as Japan where kelp remains the Number 1 supplement.
Use 1/4 teaspoon with some juice 2 times daily
2- dandelion leaves were used to treat liver problems; to treat kidney disease, swelling, skin problems, heartburn, and stomach upset and to treat digestive disorders, and breast problems.
Use 1 tea spoon of the powdered herb in half cup of boiling water for 5 minutes, let it cool and drink before meal 3 times daily.
3 – Wild duckweed
Mix 1 part Wild duckweed with 1 part honey and eat 1 teaspoon of the mix twice a day 1 hour after meals.
Lines of handling the problem
A - Start skin sensitization
1 - Casterine liniment.. is skin sensitizer herbs. Apply the liniment on the affected area of the skin and rub the area in circular way for at least 10 minutes every time, and stand on the sun for 10 minutes until it get pink and dry..
B – Apply the active and vital medication
1 - No - vitiligo tincture spray: it is the blend of carefully selected herbs used for centuries to treat vitiligo patient with success rate from 60 – 90 %. Work locally and specifically on the depigmented skin cells to neutralize its pigmentation; and get rid of the skin discoloration

How to use: Apply the tincture on the affected area of the skin directly, or using clean cotton bud (ear swab) immerse on the tincture, then apply enough to sensitive areas like eye or mouth corner or any other sensitive areas.
Expose the affected area of the skin to the early morning Sun for about 10 minutes to let Psoralen photochemotherapy work - Also known as psoralen and ultraviolet therapy, or PUVA therapy, this is probably the most effective treatment for vitiligo available, work perfectly and efficiently. If no sun around, you can use UVlamp for that purpose. Good result would be clear within 1 week of regular medication.

2 – Ginko powder tea used to enhance a clear mind and improve the power of concentration. Increasing circulation to the brain and other parts of the body as well as exerting a protective action on nerve cells. Those patients whose had Vitiligo marks on face area and consumed Ginkgo had the spread halted where as people with similar condition but people in placebo group did not face any reversals.
Ginkgo extract seems to be a simple, safe, and fairly effective therapy for arresting the progression of the disease."

3 - Psoralea Fruit.
Psoralea seeds tea
The dosage is for adults: use 10 grams of raw herb twice a day. Please put the seeds into a cup, then put 50-100 ml boiling water into the cup and stir it with spoon. You will get Vitiligo tea; drink it when it is warm.

IN CASE if you have any skin irritation due use your medication, you can use fresh Aloe vera jell

Eat right for your blood type
Some foods having good medicine to treat vitiligo:
Take some multivitamin brand full of vitamin, minerals, and essential elements for good health
Also try to eat the following vegetables and fruits like parsley, fennel, figs, clementines, mandarins, grapefruit and celery where full of Psoralen
Foods to avoid (or eat in a moderate)
· Foods high in salt (promote dehydration).
· Foods high in protein (increases body heat)
· Avoid foods yeast based
· Meat fats
· The fried
· Avoid iced drinks
· Soft drinks and sweetest
· Avoid drinks bases quinine
· Avoid consuming alcohol, wine and beer
Food or food recommended:
· Vegetables' green leaves ": spinach, broccoli, raw peppers, cabbage, watercress
· Other foods: asparagus, green lentils, radishes, beans and artichokes
· Fruits: tomatoes, blackberries, cassis, lemon, orange, melon, watermelon, apricots, fresh fruit juice, dried fruit (apricots, etc.), honey ...
· Foods containing vitamin E (natural treatment of burns and speeds healing): Wheat germ oil, sunflower, olive, peanut, rapeseed, fruit dry "Peanuts, hazelnuts, almonds, Margarine and butter, eggs ...
· Other: brains, tuna fish caught in deep water and mostly fat
· Do not forget to eat garlic, onion, and Black pepper
 Our line of Medication, with our product: NO Vitiligo
Our line of Medication, with our product: NO VitiligoOur product in the form of 10 % tincture of carefully selected herbs, work locally and specifically on the depigmented skin areas to neutralize its pigmentation, and get rid of the skin discoloration with promising great cure rate
Package: 70 ml spray bottle
Price: only 15 USA Dollars + Shipping accordingly How to use:
Apply the tincture on the affected area of the skin, using clean ear cotton swap immerse on the tincture, then apply enough to wet the affected skin area, regardless its position on your body.
Expose the affected area of the skin to direct Sunrays for about 10 – 15 minutes only that let Psoralen photochemotherapy work perfectly and efficiently.Good result would be clear within 1 week of regular medication keep continue using the medication for at least 6 months or until you have good improvements
We do also have a combination of Chinese herbal formula as an effective alternative treatment for vitiligo skin disorder
Chinese medicine for the treatment of vitiligo skin disorder, there's virtually no harm in giving it a try, if you have not been responding to the traditional mainstream treatment such as steroid cream, psoralen plus ultraviolet A therapy (PUVA)
The roll of this formula were found to play a positive role through promoting adhesion and/or migration of melanocytes (the cells that give skin color) in the treatment of vitiligo also it arrest the progression of the disease as it is to induce repigmentation